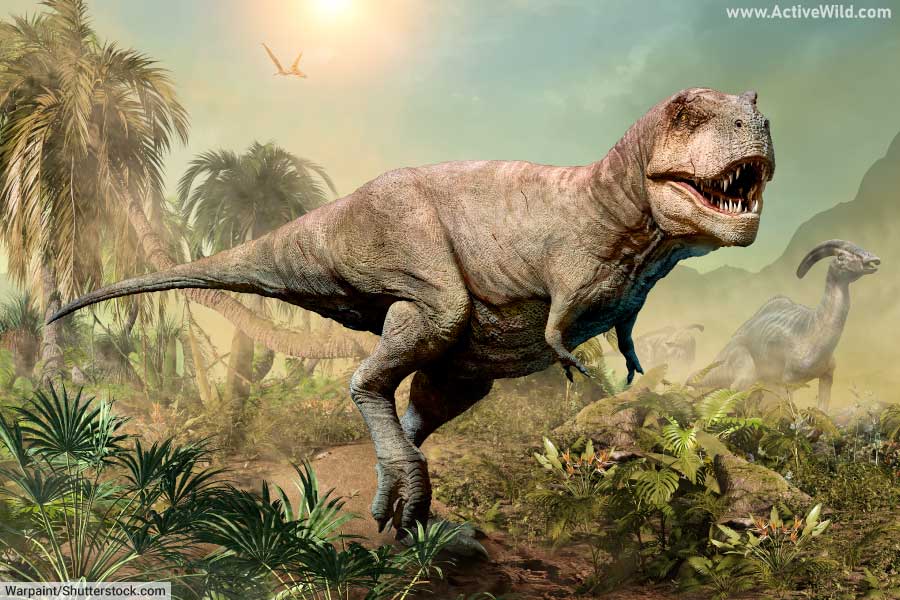
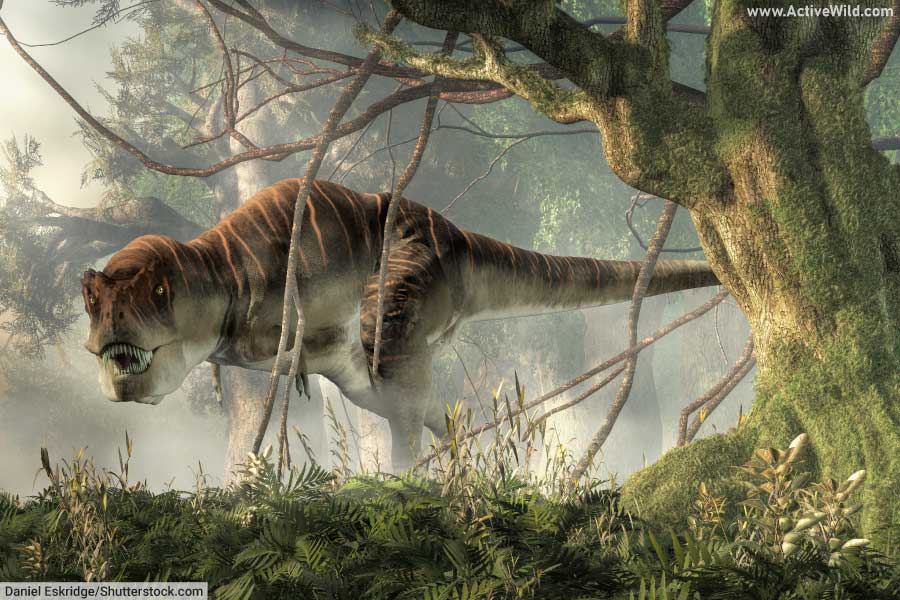
T rex, or Tyrannosaurus rex, is a species of carnivorous, theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now the western United States during the Late Cretaceous. With an estimated length of up to 13 meters / 43 feet, T. rex is one of the largest land predators that ever lived. T-rex lived alongside several other well-known dinosaurs, including Triceratops and Ankylosaurus.
T Rex: The Ultimate Guide
This page is the ultimate guide to T Rex. Continue reading to find out all you need to know about the world’s most famous dinosaur, including: when and where T Rex lived, what it ate, whether or not it had feathers, and… what was the deal with those tiny arms?
Free Printable T. Rex Worksheet PDF To Download
Test your T. rex knowledge with this FREE printable T Rex Worksheet. Click here or on the image below to download your copy. (No sign-up required.)
Page Index
- T. Rex Stats
- Description
- Bite Force
- Size
- Speed
- Feathers
- What Does Tyrannosaurus Rex Mean?
- T. Rex Or Tyrannosaurus Rex?
- What Type Of Dinosaur Was T-Rex?
- When and Where Did Tyrannosaurus Rex Live?
- Who Discovered T Rex?
- How Many T. Rex Ever Lived?
- What Did T Rex Eat?
- How Did T. Rex Hunt?
- What Did T Rex Use Its Arms For?
- T-Rex In Jurassic Park
- Top Ten T-Rex Facts
- Discover More About Prehistoric Life With Active Wild
Related Pages
- This article is part of our Dinosaur series. You can check out our main dinosaur page here: Dinosaur Facts
- Discover more dinosaurs on this page: Illustrated Dinosaur List
T Rex Stats
T. Rex Description
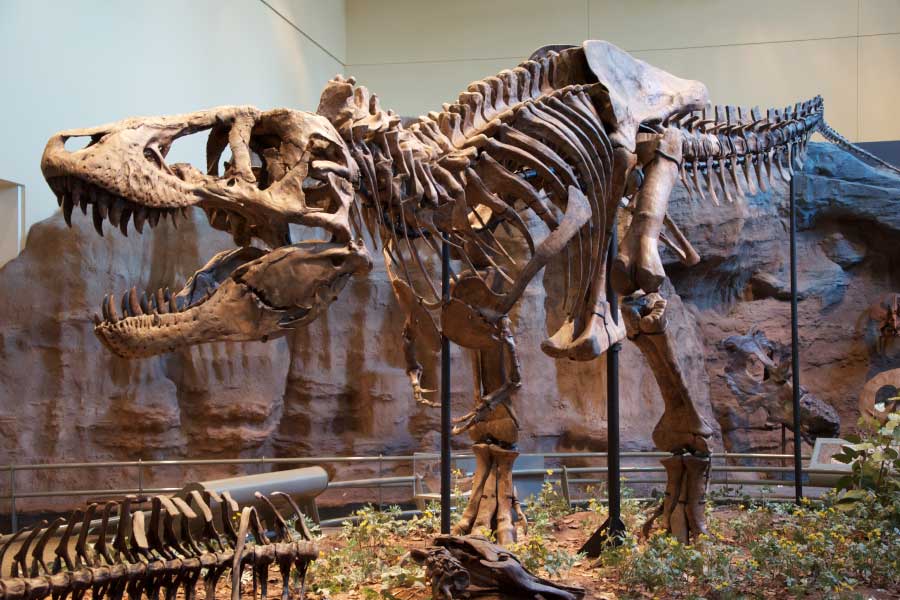
T rex was a large, predatory dinosaur. It stood on two muscular hind legs, and had a well-built body and long, powerful tail. Its arms, in relation to the size of its body, were tiny.
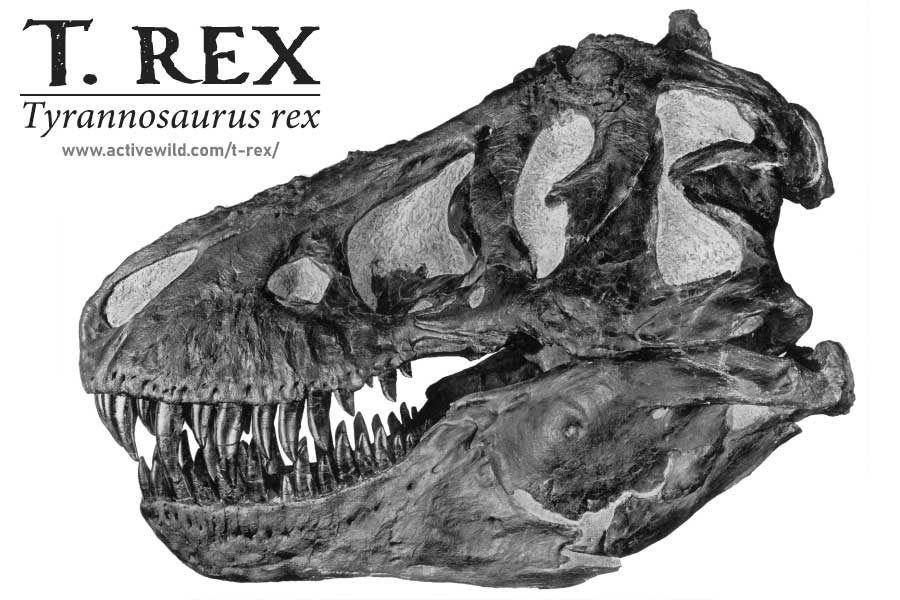
T Rex’s head was extremely large and heavily-built; the largest T. Rex skull is 5 ft. / 1.52m in length.
In the past, T rex was often depicted standing upright, with the tail propping up the body. By studying the dinosaur's skeleton, paleontologists now know that the body would normally have been held in a horizontal position, with the tail held off the ground. The dinosaur's considerable weight would have been balanced over the hips.
Claws
T Rex had two clawed fingers and a tiny, vestigial, claw-less third finger on each hand. Each foot had three main claws, with a fourth, smaller, claw located further up the foot (like a dog's dewclaw).
Teeth
T. rex’s incredibly powerful jaws were filled with 54 to 60 long, sharp teeth. T. rex’s teeth weren't all the same shape; those at the front of the mouth were built for cutting; those at the back were built for strength.
T-Rex Bite Force
T rex is estimated to have had the strongest bite force of any land animal, living or extinct. One study (source) found that a single T rex tooth positioned at the back of the jaw could exert a bite force of 35,000 to 57,000 Newtons... that’s over twice the bite force of a saltwater crocodile, which has the highest bite force of any living species.
Paleontologists can tell that T rex’s jaw muscles were extremely powerful from the way they were fixed to its skull. The skull and jaws too were built for strength. T. rex would have been able to crush bones–even the thick leg bones of other dinosaurs.
As always, clues as to T Rex’s abilities come from fossils; the remains of T Rex dung include fragments of bones that were swallowed along with the rest of the prey.
Fossilized animal droppings are known as “coprolites”.
Fossilized skeletons of Triceratops and other prey dinosaurs have broken bones that were likely to have been caused by T. Rex bites.
It’s thought that T. rex’s powerful bite allowed it to specialize in large prey, giving the dinosaur the edge over smaller, more nimble predators. The species’ bite force increased with age, which meant that juvenile T rex weren’t competing with adults for food.
T. Rex Senses and Adaptations for Hunting
It’s not just the big teeth and strong bite force that tell paleontologists that T. rex was a predator. Other clues are forward-facing eyes (the eyes of Tyrannosaurus rex were more forward-facing than those of any other tyrannosaurid), and a head shape that is much wider at the back than at the front. Both of these would have increased the dinosaur's binocular vision.
Binocular vision helps an animal judge distance – a useful skill for a hunter.
Not only is T rex thought to have had excellent eyesight, but from by the size of its olfactory bulbs (the part of the brain devoted to smell), the dinosaur is believed to have had a good sense of smell. Its acute senses would have helped T. Rex to locate and stalk prey.
T rex had a relatively short but flexible neck, allowing it to make quick changes in direction in order to grab fleeing prey.
T Rex Size
T rex was 11.4 m to 13 m (37 to 43 ft.) in length, and weighed 5.4 to 8.87 (metric) tons / 5.95 to 9.77 short tons. It stood around 3.96 m (13 ft) tall at the hips.
Many of Tyrannosaurus rex’s bones were hollow to reduce weight.
T rex weighed more than five Toyota Corollas, and, if it was around today, would be able to peer into upstairs windows with ease!
“Scotty”, the largest T rex specimen to have been discovered, had an estimated length of 13 meters / 43 feet, and an estimated maximum weight of 8.87 (metric) tonnes / 9.77 short tons.
“Sue”, the second-largest T rex specimen, had a maximum estimated length of 12.8 meters (42 ft), and an estimated weight of 8.462 (metric) tonnes / 9.33 short tons.
T rex may have been one of the largest land predators that ever lived, but it was significantly smaller than huge sauropod dinosaurs such as Brontosaurus and Argentinosaurus.
T Rex Speed
T rex is thought to have had a maximum speed of around 25 mph / 40.23 km/h, although estimates vary: some paleontologists put the top speed of this huge dinosaur closer to 45 mph / 72.42 km/h; while others make it as low as 11 mph / 17.7 km/h.
Given that Usain Bolt, the world’s fastest-recorded human, has a top speed of 27.79 mph / 44.72 km/h, and most people would struggle to reach 15 mph / 24.14 km/h, you may want to think twice before trying to out run Tyrannosaurus rex!
T. Rex Walking Speed
Studies based on trackways (fossilised T. rex tracks) suggest that the walking speed of T. rex was only around 3 to 5 miles per hour (4.83 to 8.05 km/h).
A 2021 study by Pasha A. Van Bijlert (source), which looked at the whole of T. rex's anatomy, including its long tail, concludes that the dinosaur's walking speed was just under 3 mph / 4.83 km/h – that's about the same as a human.
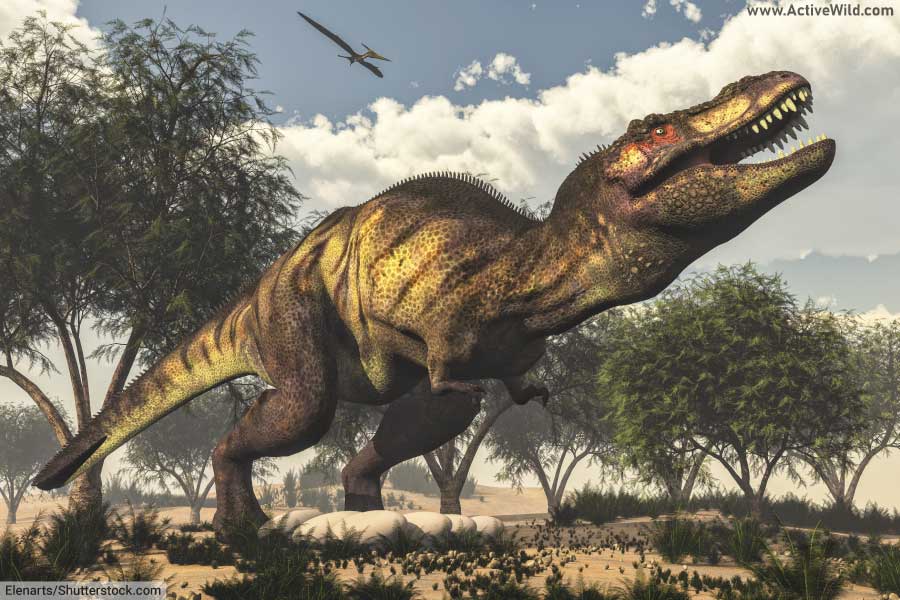
Did T Rex Have Feathers?
To this day, no T rex specimens with feathers have been found. Despite the lack of conclusive proof, some paleontologists believe that T. Rex may have been at least partially feathered, at least when young.
Other paleontologists believe that even a full-grown Tyrannosaurus Rex would have had feathers. Evidence for a feathered T rex comes in the shape of Yutyrannus, a Chinese tyrannosauroid of the early Cretaceous, which did have feathers.
Sinosauropteryx, a theropod from the early Cretaceous, is also known to have primitive feathers, suggesting that later theropods, including T rex, would have had feathers too.
What Does Tyrannosaurus Rex Mean?
The word “tyrannosaurus” means “tyrant lizard”, and “rex” means “king”, so together, Tyrannosaurus rex means “tyrant lizard king” / “king tyrant lizard”.
T. Rex Vs Tyrannosaurus Rex
The names T. rex and Tyrannosaurus rex both refer to the same dinosaur. In scientific writing, the first part of a species’ name can be shortened to an initial (to save unnecessary repetition). Therefore Tyrannosaurus rex is often shortened to T. Rex.
T. rex, T rex and T-rex are all abbreviated versions of the full name, Tyrannosaurus rex, and all refer to the same dinosaur.
T. Rex Is A Species
Tyrannosaurus rex is one of the few dinosaurs known by its full, two-word species name (Tyrannosaurus rex) rather than by its generic name (Tyrannosaurus). In other words, T. rex is an actual species, rather than a grouping that could contain more than one species.
In this way, T. rex differs from dinosaurs such as Spinosaurus and Triceratops, which are known by just their single-word, generic names.
Although various other species of genus Tyrannosaurus have been proposed, T. rex remains the only Tyrannosaurus species that is widely accepted.
Note: it’s customary to write the names of species (e.g., Tyrannosaurus rex) and genera (e.g., Tyrannosaurus) in italics.
Spinosaurus is a genus, rather than a species, whereas Tyrannosaurus rex, or T. rex, is a species.
- You can find out more about terms such as "genus" and "species" on this page: Animal Classification
What Type Of Dinosaur Was T Rex?
T Rex was a theropod dinosaur. Theropods are members of the clade Theropoda (a clade is an “evolutionary branch” of animals). The majority of theropods were predatory and bipedal (i.e., they walked on two legs).
Other theropod dinosaurs include Spinosaurus, Velociraptor, and Allosaurus.
There are still theropods living today, in the shape of birds. Birds evolved from dinosaurs, and today most scientists consider birds to be dinosaurs. (To differentiate birds from other dinosaurs, scientists often call them “non-avian dinosaurs”.)
Birds are the only dinosaurs to have survived the Cretaceous-Paleogene Extinction Event that wiped out T Rex and all of the other non-avian dinosaurs.
Like all theropod dinosaurs, T. rex was a saurischian (a member of the group Saurischia). Saurischia was one of two main dinosaur branches, the other being Ornithischia.
You can find out about theropoda, saurischia, and other types of dinosaur on these pages:
T Rex Family
T rex belongs to the family Tyrannosauridae, a group of therapod dinosaurs that lived during the Late Cretaceous Period. The family contains between three and thirteen genera; the exact number is constantly changing as new research becomes available.
The Tyrannosaur Family: Dinosaurs Related To T Rex
Other members of the family Tyrannosauridae include Lythronax, Daspletosaurus, Gorgosaurus, Albertosaurus and Tarbosaurus.
Of these, Tarbosaurus is considered to be the dinosaur most closely related to T-rex. Some paleontologists believe that this Asian Tyrannosaurid was an ancestor of T. rex.
When Did T. Rex Live?
T Rex lived from around 68 to 66 mya (million years ago), during the Maastrichtian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch (the Cretaceous Period is divided into two epochs: the Early Cretaceous and the Late Cretaceous). The species lived right up to the Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event that wiped out the non-avian dinosaurs.
The Cretaceous Period was the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era. The Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event marked the end of the Mesozoic era and the beginning of the Cenozoic Era.
- Confused by terms like "age", "epoch", "period" and "era"? Check out our Guide To The Geologic Timescale
- The extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs is thought to have been caused by an asteroid impact. You can find out more on this page: How Big Was The Asteroid That Killed The Dinosaurs?
Where Did T Rex Live?
T Rex lived in Laramidia, an island continent that eventually formed what is now western North America.
Although, at the time T rex was alive, the continents had begun to resemble their modern day form, North America was still mostly split in two by a shallow inland sea known as the Western Interior Seaway.
The Western Interior Seaway divided what is now North America into two island continents: Laramidia in the west and Appalachia to the east.
Over 50 T Rex specimens have been discovered. Many of these (including the specimen from which T rex was first identified) were found in the Hell Creek Formation, a rock formation formed in the Late Cretaceous that covers parts of Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming. T rex fossils have also been found in Canada.
Who Discovered T Rex?
Several partial T rex fossils had been found before the dinosaur had been identified, but it was American paleontologist Barnum Brown who discovered the two specimens that led to T rex being named and identified as a new species.
Brown discovered the first of these T. rex fossils in Wyoming in 1900. Two years later, he found the next, in the Hell Creek Formation at Montana.
Who Named T Rex?
Brown's fossils made their way to American paleontologist and then-president of the American Museum of Natural History, Henry Fairfield Osborn.
Osborn named the first of Brown's fossils Dynamosaurus imperiosus and the second Tyrannosaurus rex, in 1905. The following year, he realized that both fossils were of the same species, and retained his preferred name, Tyrannosaurus rex.
How Many T Rex Have Ever Lived On Earth?
T. rex was an apex predator, and by observing modern animals we know that an ecosystem can generally support only a limited number of apex predators.
So how many T. rex lived at one time, and how many T. rex ever lived?
These are questions paleontologist Dr Charles R. Marshall and his team set out to answer in a recent study. (Source)
Damuth's law states that there is an inverse relationship between body size and population density in living animals. Using this law, and by comparing T rex's likely metabolism with that of living animals (faster than a Komodo dragon, but slower than a predatory mammal), Marshall et al were able to come up with likely estimates of T rex population size.
They found that around 20,000 T. rex lived at any one time, and that the total number of T rex that ever lived was around 2.5 billion. Their research also revealed that only 1 in every 80 million T. rex that ever existed has been found as a fossil, but that this number increases to 1 in every 16,000 T rex in areas where the dinosaur was abundant.
T. rex Skeleton Fossils
Since the holotype specimen (i.e. the specimen from which the species was named) was discovered by Barnum Brown, numerous other T. rex fossils, including several almost-complete skeletons, have been found.
Near-complete (70% or more) T. rex skeletons include: "Sue", discovered in South Dakota in 1990; "Scotty", discovered in Saskatchewan in 1991; "Thomas", discovered in Montana in 2003; and "Trix", discovered in Montana in 2013.
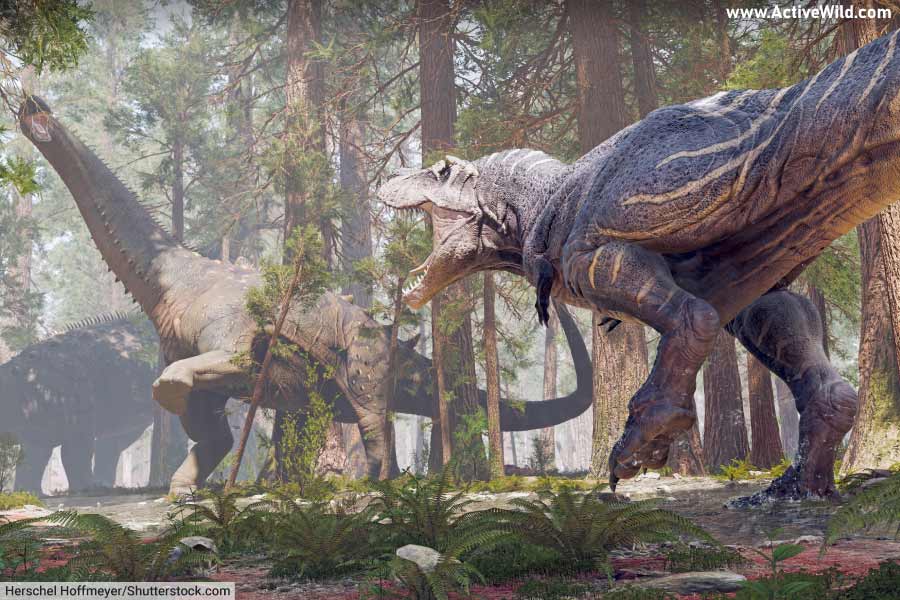
What Did T Rex Eat?
T. rex preyed on a variety of dinosaurs and other animals found in western North America in the late Cretaceous Period.
Edmontosaurus, Triceratops, Leptoceratops, Ankylosaurus, Pachycephalosaurus and smaller theropods such as Ornithomimus and Struthiomimus are all known to live alongside T rex and all were likely to have been on the menu for the large predator.
Was T Rex A Cannibal?
Some T Rex specimens have bite marks that seem to have been made by other T Rex. This may have been caused by fighting to establish dominance, cannibalism, or scavenging.
How Did T Rex Hunt?
Tyrannosaurus Rex probably used short bursts of speed to capture its prey; it was too heavy to pursue other dinosaurs over long distances.
Although T Rex probably hunted its own food, it is likely that scavenged food also made up at least part of its diet. T Rex had an excellent sense of smell, which to many scientists suggests that scavenging was actually T Rex’s principal means of finding food.
However, T rex also had excellent vision, which supports the belief that T rex was primarily a hunter rather than a scavenger; scavengers generally don’t need highly-developed vision.
Other scientists believe that T Rex’s brain was large enough for it to be able to hunt in packs (you need to be smart to work as a team).
What Did T Rex Use Its Arms For?
T Rex’s arms, which were around one fifth of the length of its legs, seem to be too small to have served any useful purpose. However, the amount of muscle attached to the arm bones suggest that the arms, although short, were strong, and probably did have a function.
There are several theories as to what T Rex’s arms were used for, including: holding prey close to the jaws when eating, and helping T Rex to get up from the ground.
One thing T rex couldn’t do with its arms was use them to pass food to its mouth; they were too short.
T. Rex In Jurassic Park (Spoilers Alert!)
In the Jurassic Park (and subsequent Jurassic World) movie franchise, T. rex is one of the principal (non-human) antagonists. However, the dinosaur also serves as a type of "antihero", making several plot-twisting interventions that ensure a happy ending for the films' human protagonists.
One of the most famous Jurassic Park scenes featuring T. rex is at the climax of the ill-fated car tour of the park. Before the tyrannosaur eventually strikes, its footsteps are seen making ripples in glasses of water.
In the film's sequel, "The Lost World: Jurassic Park", an escaped T. rex rampages through San Diego. Although T. rex comes to a sticky end at the hands (and teeth) of Spinosaurus in Jurassic Park III, the dinosaur is back saving the day (with the help of Velociraptors and a Mosasaurus) at the climax of Jurassic World!
Top Ten T-Rex Facts
- Tyrannosaurus rex means ‘King Tyrant Lizard’. The name Tyrannosaurus rex is often abbreviated to ‘T. Rex’.
- T. Rex lived in western North America, which at that time was an island continent known as Laramidia.
- Tyrannosaurus rex lived in the Late Cretaceous Period, around 68 to 66 million years ago.
- T Rex may have lived right up to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that wiped out all of the non-avian dinosaurs.
- T rex was 11.4 m to 13 m (37 to 43 ft.) in length. It stood around 3.96 m / 13 ft. tall at the hips.
- T Rex weighed 5.4 to 8.87 (metric) tons / 5.95 to 9.77 short tons.
- T Rex had between 54 and 60 long, sharp teeth. The largest T Rex tooth found is over 30 cm / 12 in. long (including the root)
- Some paleontologists believe that T Rex may have had feathers, which had appeared in other, earlier theropod dinosaurs.
- Most of the evidence points towards T Rex being a hunter, but some paleontologists think that it would have found most of its food by scavenging.
- The arms of T. rex were one fifth the length of its legs and were too short to carry food to the mouth.
Discover More With Active Wild
- Cretaceous Period Dinosaurs List With Pictures & Facts: Discover The Dinosaurs That Lived In The Cretaceous Period
- Jurassic Dinosaurs List: Discover The Dinosaurs That Lived In The Jurassic Period
- Triassic Dinosaurs List with Pictures & Facts: Discover the Dinosaurs of the Triassic Period!
- Dinosaur Identification: Find Dinosaurs By Their Characteristics
- Cool Dinosaurs List With Pictures And Interesting Facts
- Famous Dinosaurs List With Pictures And Interesting Facts
- How Long Ago Were Dinosaurs Alive? Amazing Facts & Figures